The heart is a vital organ in the human body, responsible for pumping blood and ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all the tissues. Located in the chest cavity, the heart is composed of both striated and non-striated cardiac muscle. Its four chambers – the right ventricle, left ventricle, right atrium, and left atrium – work together to maintain the circulation of blood throughout the body.
One of the key functions of the heart is to receive blood from the veins and pump it into the arteries, which then distribute it to various parts of the body. This continuous cycle ensures that all organs and tissues receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients for optimal functioning. Additionally, the heart plays a crucial role in removing waste products from the body.
The heartbeat is regulated by the cardiac conduction system, which consists of the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and bundle of His. These electrical signals coordinate the rhythm of heartbeats, ensuring that the heart functions in a synchronized and efficient manner.
Heart diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that can affect the health and function of the heart. Some common examples include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, valvular heart disease, and congenital heart defects. These conditions can have serious implications for overall health and may require specialized medical guidance for proper management.
Treatment for heart diseases varies depending on the specific condition but often involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Maintaining heart health is crucial for overall well-being. There are several key factors that contribute to a healthy heart:
- Adopting a healthy diet: A balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help support heart health.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Avoiding smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can have a positive impact on heart health.
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels: High blood pressure and cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease. Regular monitoring and appropriate management of these factors are essential.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can strain the heart and increase the risk of heart disease. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise is beneficial.
- Keeping blood sugar levels within a normal range: Diabetes and high blood sugar levels can contribute to heart disease. Monitoring blood sugar levels and managing diabetes effectively can help protect heart health.
By prioritizing these factors and making conscious lifestyle choices, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy heart. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are also essential for monitoring heart health and identifying any potential issues early on.
Remember, a healthy heart is the foundation for overall well-being, and investing in heart health today can lead to a healthier and happier future.

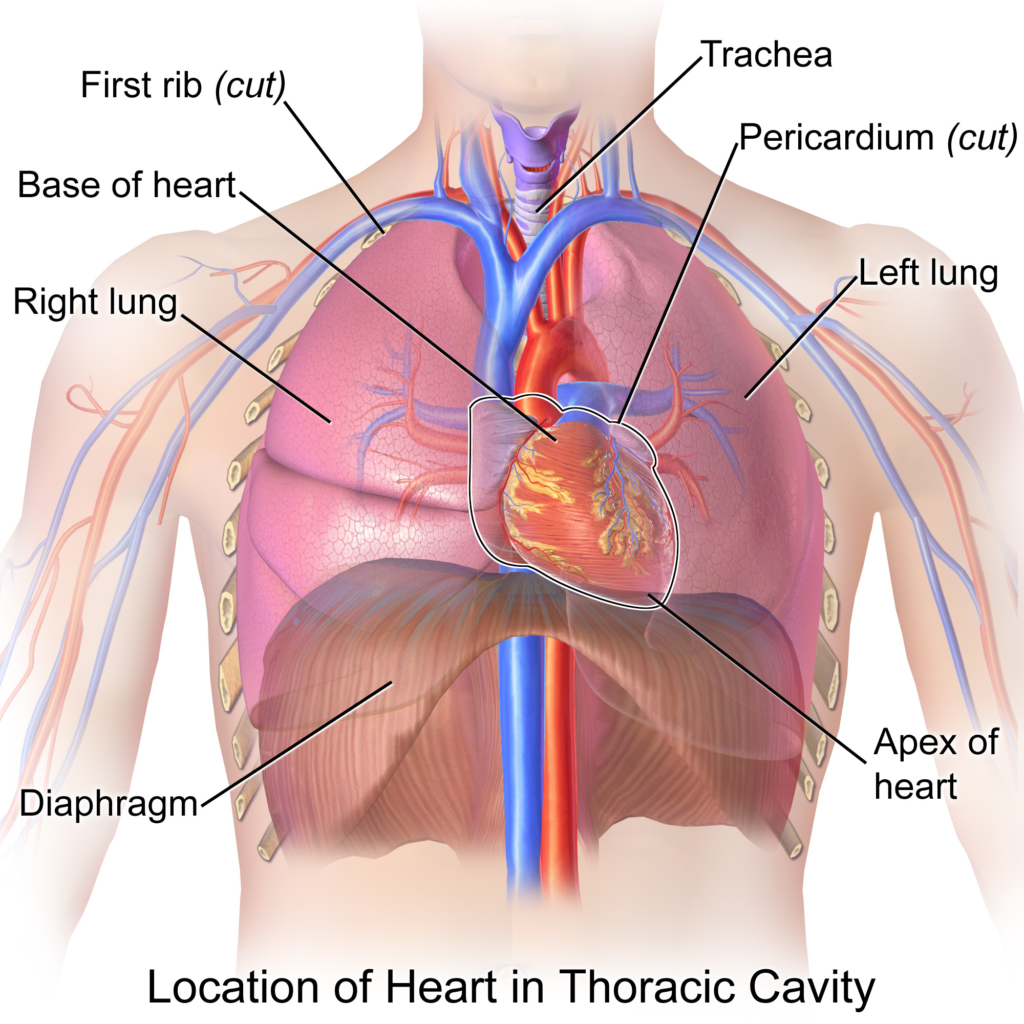
القلب هو عضو عضلي مهم في جهاز الدورة الدموية في الجسم. يقع القلب في تجويف الصدر ويتكون من عضلة القلب المخططة وغير المشطبة. وظيفة القلب هي ضخ الدم إلى جميع أنحاء الجسم لنقل الأكسجين والمواد المغذية إلى الأنسجة وإزالة النفايات الضارة من الجسم.
يتكون القلب من أربعة أجنحة رئيسية: البطين الأيمن والبطين الأيسر والأذين الأيمن والأذين الأيسر. يعمل الأذينان على استقبال الدم من الأوردة وتفريغه في البطينين، بينما يعمل البطينان على ضخ الدم إلى الشرايين لتوزيعها في الجسم.
يتم تنظيم نبضات القلب بواسطة جهاز القلب، الذي يشمل عقدة الجيب الأذيني (SA node) وعقدة الأذين البطينية (AV node) ونظام الألياف القلبية. يتم تنظيم هذه النبضات بواسطة إشارات كهربائية تنتقل عبر الألياف القلبية، مما يسمح بتنظيم إيقاع ضربات القلب.
أمراض القلب هي مجموعة واسعة من الحالات التي تؤثر على صحة ووظيفة القلب. من أمثلة أمراض القلب الشائعة: أمراض الشرايين التاجية، وارتفاع ضغط الدم، والتاهيل الجزئي للصمامات القلبية، وأمراض القلب الخلقية. يتطلب علاج أمراض القلب توجيهًا طبيًا متخصصًا وقد يشمل الأدوية والتغييرات في نمط الحياة والإجراءات الجراحية في بعض الحالات.
من الأمور المهمة للحفاظ على صحة القلب العناية بالنظام الغذائي الصحي، وممارسة النشاط البدني بانتظام، والامتناع عن التدخين، والتحكم في ضغط الدم ومستويات الكولسترول، وإدارة الوزن بشكل صحي، والحفاظ على مستويات السكر في الدم ضمن النطاق الطبيعي.
القلب هو عضو عضلي مهم يتواجد في تجويف الصدر ويقوم بضخ الدم في جميع أنحاء الجسم. يتكون القلب من عدة أجزاء وتجاويف تعمل معًا لتحقيق وظيفته الحيوية. هنا هي أجزاء القلب الرئيسية:
- الأذين الأيمن (Right Atrium): يستقبل الدم من الأوردة الرئوية، وهي الأوعية الدموية التي تحمل الدم غير المؤكسج من الجسم.
- الأذين الأيسر (Left Atrium): يستقبل الدم من الأوردة الرئوية الأيسر وهي الأوعية الدموية التي تحمل الدم المؤكسج من الرئتين.
- البطين الأيمن (Right Ventricle): يستقبل الدم من الأذين الأيمن ويضخه في الشريان الرئوي لتوصيله إلى الرئتين للتأكسج.
- البطين الأيسر (Left Ventricle): يستقبل الدم من الأذين الأيسر ويضخه في الشريان الأورطي لتوزيعه في جميع أنحاء الجسم.
هناك صمامات بين الأذينات والبطينات تعمل على منع انسكاب الدم في الاتجاه العكسي. وهناك أيضًا صمامين في نهاية البطينات يمنعان انسكاب الدم من الشرايين إلى الأذينات.
يعمل القلب عن طريق ضرباته المتتابعة والمنتظمة. تبدأ هذه الضربات بإشارة كهربائية تنشأ في عقدة الجيب الأذيني، ثم تنتقل إلى عقدة الأذين البطيني ومن ثم عبر حزمة هيس لتنتشر في العضلات القلبية وتحفز انقباضها.
هذا هو تشريح عام للقلب، ولكن يجب ملاحظة أن هناك تفاصيل أكثر دقة في تركيب القلب وتشريحه.