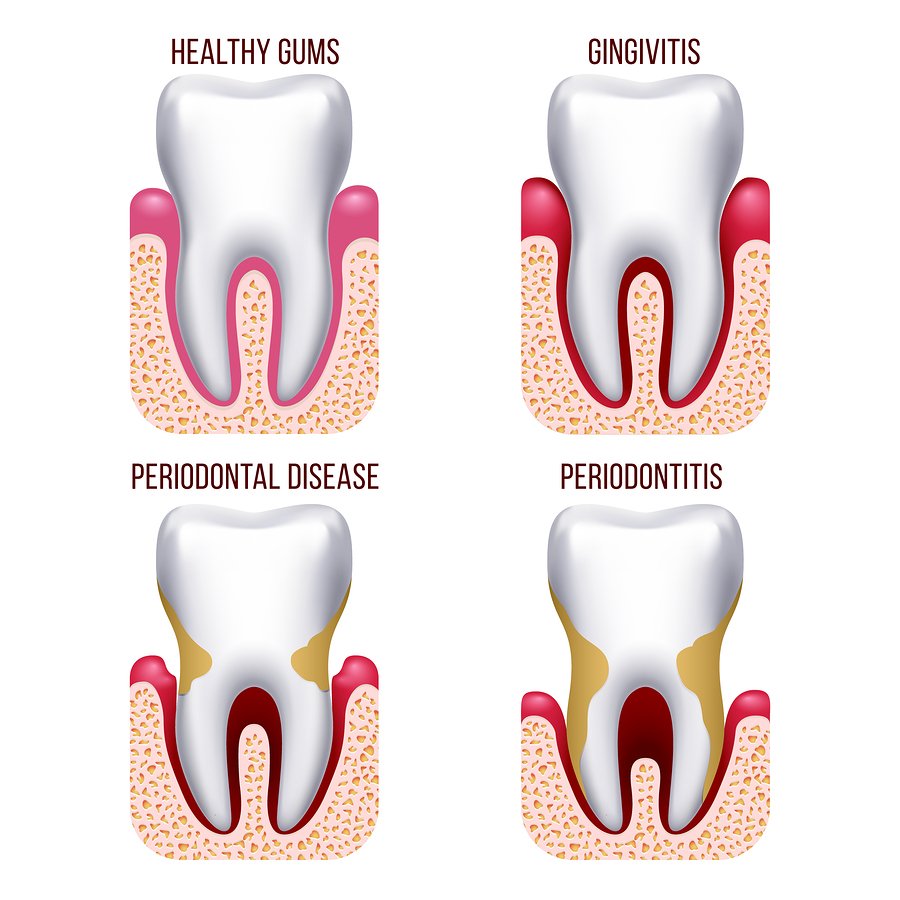
Gingivitis is a common form of gum disease that affects many individuals. It occurs when plaque, a combination of bacteria and tartar, builds up on the teeth and gums. The result is inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gums. People with gingivitis may also experience itching or pain while brushing.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious condition called periodontitis. Periodontitis occurs when the inflammation spreads to the deeper tissues surrounding the teeth and the bone. As plaque continues to build up, it starts to destroy the tissues and bone, leading to gum recession and potential tooth loss.
There are several signs to watch out for when it comes to periodontitis. Patients may notice bleeding gums during brushing, gum recession where the gum line starts to pull away from the teeth, and the formation of periodontal pockets, which are spaces between the teeth and gums.
It is important to address gum disease as early as possible to prevent further damage. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, and professional cleanings can help prevent and treat gingivitis and periodontitis.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of gum disease, it is best to consult with a dental professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options. Taking care of your oral health is crucial for maintaining a healthy smile and overall well-being.

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, refers to a group of conditions that affect the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums and the bone. These diseases cause inflammation in the tissues and can eventually lead to tissue damage and tooth loss if not properly treated. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of gum diseases, their symptoms, and causes:
Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the most common form of gum disease. It is caused by the buildup of plaque (tartar and bacteria) on the surface of the teeth and around the gums, resulting in inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gums. The affected individual may experience itching or pain while brushing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis.
Periodontitis: Periodontitis occurs when inflammation spreads to the deeper tissues surrounding the teeth and the bone. Continuous plaque buildup leads to the destruction of tissues and bone, eventually resulting in gum recession and tooth loss. Patients may notice bleeding gums during brushing, gum recession, and the formation of periodontal pockets.
Immune-related gum disease: Weakened immune systems can worsen gum inflammation or cause more severe symptoms. This can include individuals with conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Hormonal gum disease: Gums are also affected by hormonal changes during periods such as pregnancy, puberty, and hormonal changes associated with sexual diseases. Individuals exposed to these factors may experience irritation, swelling, and bleeding gums.
Causes of Gum Disease:
- -Poor Oral Hygiene: The primary cause of gum disease is inadequate oral hygiene. When plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria, builds up on the teeth and along the gumline, it can lead to gum inflammation and infection.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco can increase the risk of gum disease. Tobacco use weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum disease. Certain genetic variations can make them more susceptible to gum inflammation and the progression of the disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as oral contraceptives, antidepressants, and certain heart medications, can affect oral health and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer can weaken the immune system and make individuals more susceptible to gum disease.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can weaken the immune system and compromise gum health.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums, giving the teeth a longer appearance
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the bite or the way the teeth fit together
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Changes in the fit of denture1s
- Complications of Untreated Gum Disease:
- Tooth Loss: As gum disease progresses, the infection can destroy the tissues and bone supporting the teeth, leading to tooth loss.
Gum Recession: Gum disease can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and increasing tooth sensitivity.
Abscesses: Pockets of pus can develop around the teeth, resulting in painful abscesses.
Systemic Health Risks: There is a growing body of evidence linking gum disease to various systemic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular dental visits allow for early detection and treatment of gum disease.
- Professional Cleanings: Professional dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be effectively removed by brushing and flossing alone.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding tobacco use, eating a balanced diet, and managing chronic conditions can help reduce the risk of gum disease.
- Scaling and Root Planing: In cases of advanced gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be necessary to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the tooth roots.
- Surgical Treatments: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as gum grafting, flap surgery, or bone grafting may be required to restore gum health and repair damaged tissues.
It’s important to note that early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial to preventing its progression and minimizing potential complications. Regular dental care, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle are key to maintaining optimal gum health.